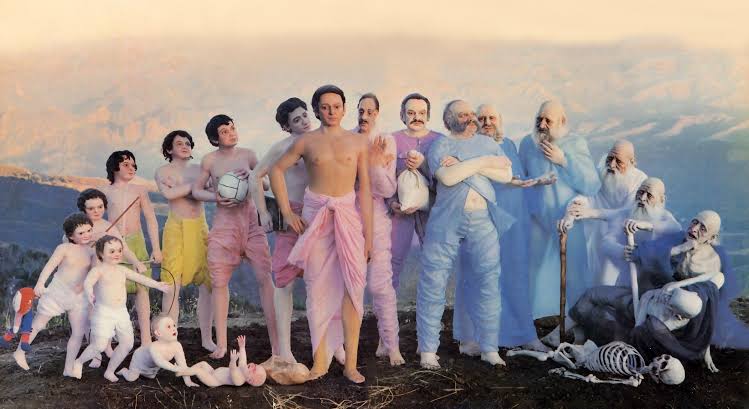
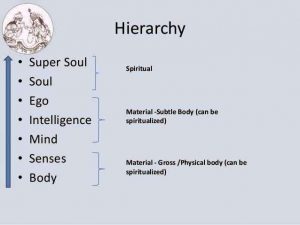
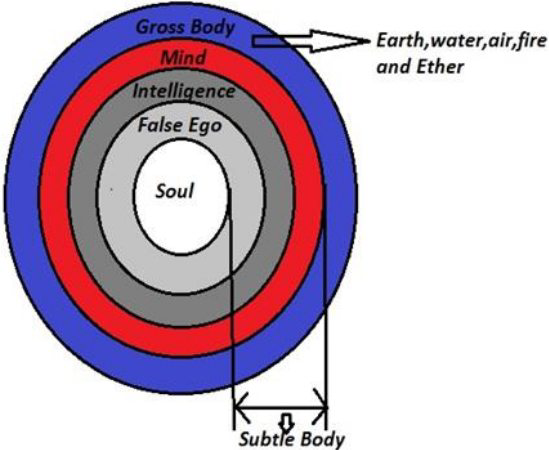
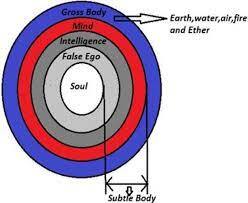
Five levels of ego covering the self.
““Within the body there are five different departments of existence, known as anna-maya, prāṇa-maya, mano-maya, vijñāna-maya, and at last ānanda-maya. [These are enumerated in the Brahmānanda-vallī of the Taittirīya Upaniṣad.] In the beginning of life, every living entity is food conscious. A child or an animal is satisfied only by getting nice food. This stage of consciousness, in which the goal is to eat sumptuously, is called anna-maya. Anna means ‘food.’ After this one lives in the consciousness of being alive. If one can continue his life without being attacked or destroyed, one thinks himself happy. This stage is called prāṇa-maya, or consciousness of one’s existence. After this stage, when one is situated on the mental platform, that consciousness is called mano-maya. The material civilization is primarily situated in these three stages — annamaya, prāṇa-maya and mano-maya. The first concern of civilized persons is economic development, the next concern is defense against being annihilated, and the next consciousness is mental speculation, the philosophical approach to the values of life.
“If by the evolutionary process of philosophical life one happens to reach the platform of intellectual life and understands that he is not this material body but is a spirit soul, he is situated in the vijñāna-maya stage. Then, by evolution of spiritual life, he comes to understand the Supreme Lord, or the Supreme Soul. When one develops his relationship with Him and executes devotional service, that stage of life is called Kṛṣṇa consciousness, the ānanda-maya stage. Ānanda-maya is the blissful life of knowledge and eternity. As it is said in the Vedānta-sūtra, ānanda-mayo ’bhyāsāt. The Supreme Brahman and the subordinate Brahman, or the Supreme Personality of Godhead and the living entities, are both joyful by nature. As long as the living entities are situated in the lower four stages of life — anna-maya, prāṇa-maya, mano-maya and vijñāna-maya — they are considered to be in the material condition of life, but as soon as one reaches the stage of ānanda-maya, he becomes a liberated soul. This ānanda-maya stage is explained in the Bhagavad-gītā as the brahma-bhūta stage. There it is said that in the brahma-bhūta stage of life there is no anxiety and no hankering. This stage begins when one becomes equally disposed toward all living entities, and it then expands to the stage of Kṛṣṇa consciousness, in which one hankers to render service unto the Supreme Personality of Godhead. This hankering for advancement in devotional service is not the same as hankering for sense gratification in material existence. In other words, hankering remains in spiritual life, but it becomes purified. When our senses are purified, they become freed from all material stages, namely anna-maya, prāṇa-maya, mano-maya and vijñāna-maya, and they become situated in the highest stage — ānanda-maya, or blissful life in Kṛṣṇa consciousness.
“The Māyāvādī philosophers consider ānanda-maya to be the state of being merged in the Supreme. To them, ānanda-maya means that the Supersoul and the individual soul become one. But the real fact is that oneness does not mean merging into the Supreme and losing one’s own individual existence. Merging into the spiritual existence is the living entity’s realization of qualitative oneness with the Supreme Lord in His aspects of eternity and knowledge. But the actual ānanda-maya (blissful) stage is attained when one is engaged in devotional service. That is confirmed in the Bhagavad-gītā: mad-bhaktiṁ labhate parām. The brahma-bhūta ānanda-maya stage is complete only when there is the exchange of love between the Supreme and the subordinate living entities. Unless one comes to this ānanda-maya stage of life, his breathing is like the breathing of a bellows in a blacksmith’s shop, his duration of life is like that of a tree, and he is no better than the lower animals like the camels, hogs and dogs.””
Source:A.C. Bhaktivedanta Swami Prabhupada (2014 edition), “Srimad Bhagavatam”, Tenth Canto, Chapter 87 – Text 17