Charateristics of a Purana and types of Purana.
“The ten subjects of a great Purāṇa are also described in the Second Canto of Śrīmad-Bhāgavatam (2.10.1):
śrī-śuka uvāca atra sargo visargaś ca
sthānaṁ poṣaṇam ūtayaḥ manvantareśānukathā
nirodho muktir āśrayaḥ
“Śrī Śukadeva Gosvāmī said: In the Śrīmad-Bhāgavatam there are ten divisions of statements regarding the following: the creation of the universe, subcreation, planetary systems, protection by the Lord, the creative impetus, the change of Manus, the science of God, returning home (back to Godhead), liberation and the summum bonum.”
According to Śrīla Jīva Gosvāmī, Purāṇas such as Śrīmad-Bhāgavatam deal with these ten topics, whereas lesser Purāṇas deal with only five. As stated in Vedic literature:
sargaś ca pratisargaś ca vaṁśo manvantarāṇi ca
vaṁśānucaritaṁ ceti purāṇaṁ pañca-lakṣaṇam
“Creation, secondary creation, the dynasties of kings, the reigns of Manus and the activities of various dynasties are the five characteristics of a Purāṇa.” Purāṇas covering five categories of knowledge are understood to be secondary Purāṇic literature.
Śrīla Jīva Gosvāmī has explained that the ten principal topics of Śrīmad-Bhāgavatam are found within each of the twelve cantos. One should not try to assign each of the ten topics to a particular canto. Nor should the Śrīmad-Bhāgavatam be artificially interpreted to show that it deals with the topics successively. The simple fact is that all aspects of knowledge important to human beings, summarized in the ten categories mentioned above, are described with various degrees of emphasis and analysis throughout the Śrīmad-Bhāgavatam.
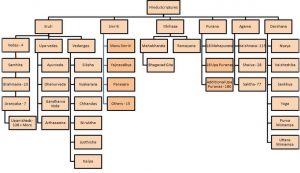
The eighteen major Purāṇas are the Brahma, Padma, Viṣṇu, Śiva, Liṅga, Garuḍa, Nārada, Bhāgavata, Agni, Skanda, Bhaviṣya, Brahma-vaivarta, Mārkaṇḍeya, Vāmana, Varāha, Matsya, Kūrma and Brahmāṇḍa Purāṇas.
The Brahma Purāṇa consists of ten thousand verses, the Padma Purāṇa of fifty-five thousand, Śrī Viṣṇu Purāṇa of twenty-three thousand, the Śiva Purāṇa of twenty-four thousand and Śrīmad-Bhāgavatam of eighteen thousand. The Nārada Purāṇa has twenty-five thousand verses, the Mārkaṇḍeya Purāṇa nine thousand, the Agni Purāṇa fifteen thousand four hundred, the Bhaviṣya Purāṇa fourteen thousand five hundred, the Brahma-vaivarta Purāṇa eighteen thousand and the Liṅga Purāṇa eleven thousand. The Varāha Purāṇa contains twenty-four thousand verses, the Skanda Purāṇa eighty-one thousand one hundred, the Vāmana Purāṇa ten thousand, the Kūrma Purāṇa seventeen thousand, the Matsya Purāṇa fourteen thousand, the Garuḍa Purāṇa nineteen thousand and the Brahmāṇḍa Purāṇa twelve thousand. Thus the total number of verses in all the Purāṇas is four hundred thousand. Eighteen thousand of these, once again, belong to the beautiful Bhāgavatam.
“After compiling the eighteen Purāṇas, Vyāsadeva, the son of Satyavatī, composed the entire Mahābhārata, which contains the essence of all the Purāṇas. It consists of over one hundred thousand verses and is filled with all the ideas of the Vedas. There is also the account of the pastimes of Lord Rāmacandra, spoken by Vālmīki — an account originally related by Lord Brahmā in one billion verses. That Rāmāyaṇa was later summarized by Nārada and related to Vālmīki, who further presented it to mankind so that human beings could attain the goals of religiosity, sense gratification and economic development. The total number of verses in all the Purāṇas and itihāsas (histories) is thus known in human society to amount to 525,000.”
Source: A.C. Bhaktivedanta Swami Prabhupada (2014 edition), “Srimad Bhagavatam”, Twelth Canto, Chapter 07 – Text 09-10 & 23-24, Chapter 13 – Text 04-09.